A Coding Portion Of A Gene
The coding region of a gene also known as the coding sequence or CDS from Coding DNA Sequence is that portion of a genesDNA or RNA composed. The production of mRNA entails the removal of the noncoding sequences from the initial RNA transcript and the splicing together of the coding sequences.
The coding region of a gene also known as the CDS from coding sequence is the portion of a genes DNA or RNA that codes for protein.
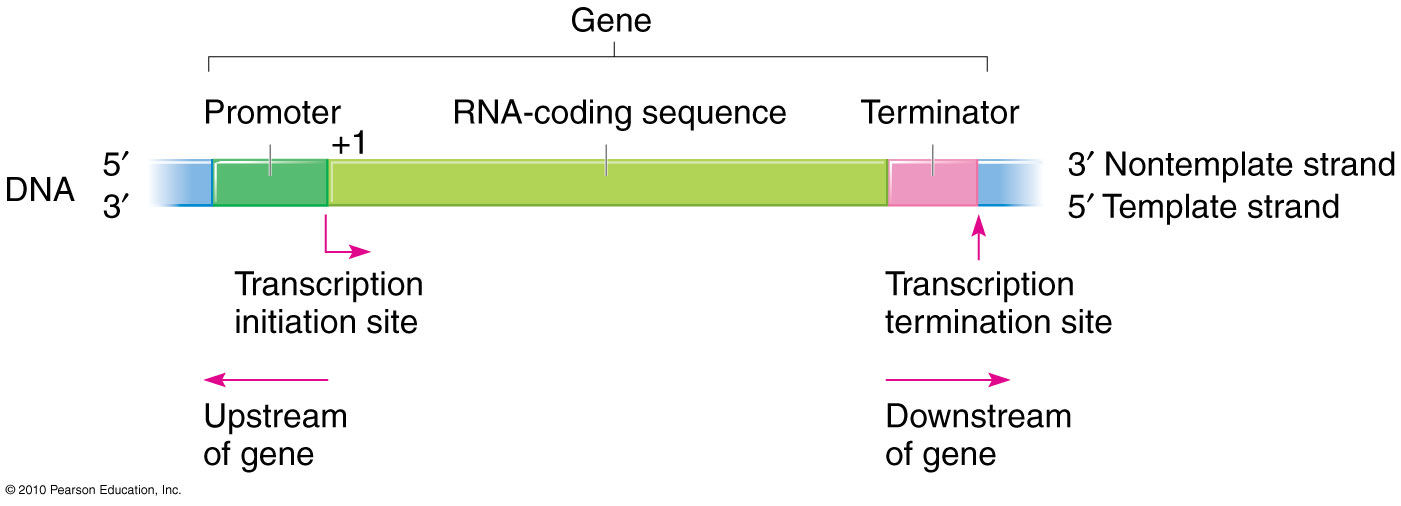
A coding portion of a gene. The coding portion of a gene involved in making a protein is known as exon or exonic sequences. As we have seen eucaryotic genes usually consist of short coding sequences of DNA exons separated by much longer noncoding sequences introns. In the genetic code each three nucleotides in a row count as a triplet and code for a single amino acid.
14 PTS The following DNA sequence is the transcribed portion of a very short protein-coding gene from a eukaryote. The relationship between a nucleotide codon and its corresponding amino acid is called the genetic code. ATATGCTACGGTATGATAGG TGACTC TGATATCAGGCCATCGATGTAAGA 3 3.
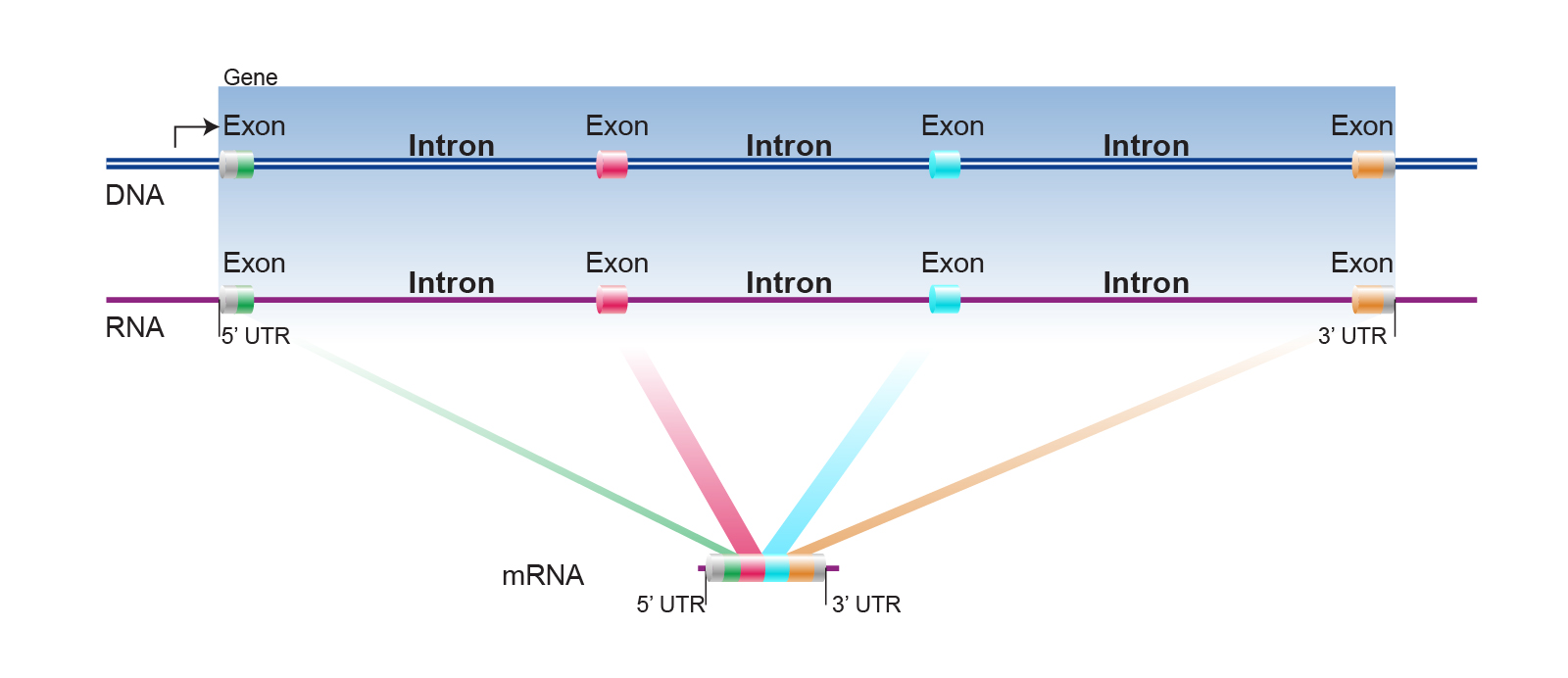
Introns are the segments of genes that are present in the primary transcript or precursor RNA but are removed by splicing in the production of mature RNA. The genetic code is the sequence of nucleotide bases in nucleic acids DNA and RNA that code for amino acid chains in proteins. In particular the protein-coding regions or genes are a subset of the sequences in exons.
NHGRI A piece of. In addition to the ncRNA molecules that are encoded by discrete genes the initial transcripts of protein coding genes usually contain extensive noncoding sequences in the form of introns 5-untranslated regions 5-UTR and 3-untranslated regions 3-UTR. DNA polymerase binds at the origin of the replication site.
It carries genetic instructions for the functioning growth development and reproduction of all known organisms. When a particular gene needs to be expressed the nucleotide sequence for the gene can be found on the coding strand but the transcription of that gene takes place on the non-coding strand also. For any given protein-coding transcript of a gene a portion of that transcript will be the coding sequence CDS the part that is actually translated into protein.
Replication is completed at the termination region of DNA. RNA contains the nucleotides adenine guanine cytosine and uracil U. Exons include both the untranslated regions and the protein-coding translated regions.
Determining the pattern and timing of gene expression can be accomplished by replacing the coding portion of the gene under study with a reporter gene. Some introns are known to affect gene expression. Coding DNA strand is one which codes for mRNA that will be.
DNA consists of the four nucleotide bases. Coding portions of genes that remain after mRNA splicing and are later translated into proteins are called exons Choice A sequence of nucleotides in DNA is copied to a sequence of nucleotides in mRNA. Each amino acid is defined by a three-nucleotide sequence called the triplet codon.
Genetic code is the term we use for the way that the four bases of DNA--the A C G and Ts--are strung together in a way that the cellular machinery the ribosome can read them and turn them into a protein. A portion of the sequence from the DNA coding strand of the myoglobin gene from a species of mollusk is shown below. NCI3 A portion of a gene that does not code for amino acids.
Gene is a segment of DNA that gives. Double helixes are separated and unwound. The number of proteins coding sequences G-value is not predictive of morphological complexity among eukaryotic organisms.
The parts of the gene sequence that are expressed in the protein are called exons because they are expressed while the parts of the gene sequence that are not expressed in the protein are called introns because they come in between the exons. Assuming that coding portion of a gene refers to the mature mRNA resulting from post-transcriptional modification non-coding introns and unused. Adenine A guanine G cytosine C and thymine T.
DNA or Deoxyribonucleic acid is a heredity molecule made of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. In most cases the expression of the reporter gene is then monitored by tracking the fluorescence or enzymatic activity of its protein product pp. The promoter for this gene is to the left of this seque Intron 5.
Different genes have a different number of exons. What is the difference between the coding and noncoding regions of a gene. TATACGATGCCATACTATCCACTGAGAC TATAG TCCGGTAGCTACATTCT5 a Label the.
Different genes alleles isoforms have different lengths but the length of the CDS will be a multiple of 3 bases. Identify the correct open reading frame orf and give the amino acid sequence for the first few encoded amino acids. When three continuous nucleotide bases code.
Ribosomes participating in production of proteins. The portion of the genome that codes for a protein or an RNA is referred to as a gene. Given the different numbers of letters in the mRNA 4 A U C G and protein alphabets 20 different amino acids one.
Within most protein-coding genes of the human genome the length of intron sequences is 10- to 100-times the length of. The non-protein coding portion of eukaryotic genomes can accurately be referred to as junk DNA because it has no impact on the phenotype of an organism. This can further assist in mapping the human genome and developing gene therapy.
Its a chain of nucleotides that are conserved and arranged loosely to allow transcription. The portion of the DNA is also known as a gene - The coding section. Those genes that code for proteins are composed of tri-nucleotide units called codons each coding for.

Module 1 Introduction Lecture 1 Role Of Genes Within Cells Genetic Code Etc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 1 6 1 Regulatory Elements Gene Expression Is A Complex Multi Step Process Amongst Various Steps Involved Transcription Initiation Is A Vital Key

Vdj Gene Segments Coding For The Antibody Heavy Chain Variable Region Download Scientific Diagram

Gene Components Genes Have Promoter Regions Which Occur Upstream From Download Scientific Diagram

Panel A Shows The Structure Of A Prokaryotic Gene The Protein Coding Download Scientific Diagram

File Gene Structure Eukaryote 2 Annotated Svg Wikipedia

Panel A Shows The Structure Of A Prokaryotic Gene The Protein Coding Download Scientific Diagram
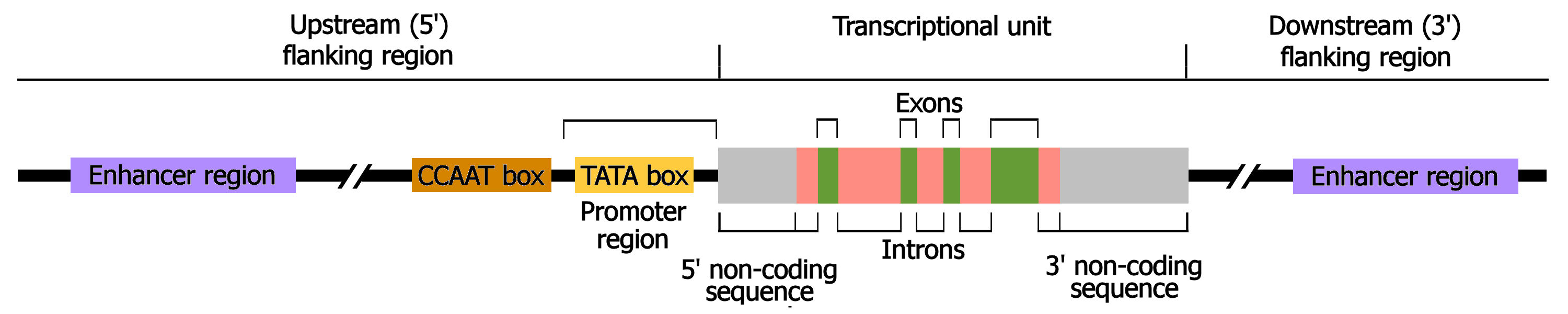
Organization Of A Eukaryotic Gene Region

Schematic Representation Of Gene Structure And Expression Notes Download Scientific Diagram
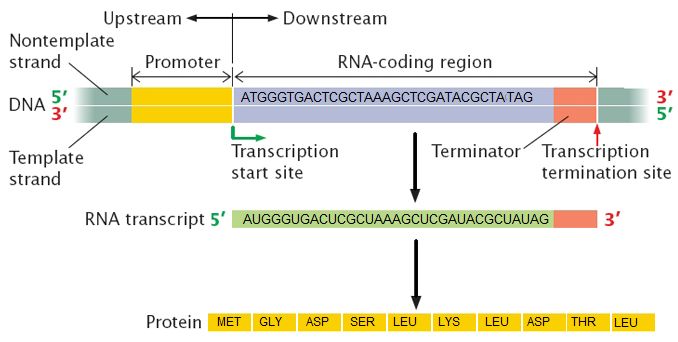
17 1 The Flow Of Genetic Information Biology Libretexts
4 How Genes Function Objectives By The End Of This Session The Student Should Be Able To Use The Genetic Code To Translate Coding Sequences Calculate The Number Of Codons And Amino Acids From The Number Of Bases Name The Main Sites Of
What S The Difference Between Cds And Orf

Posting Komentar untuk "A Coding Portion Of A Gene"